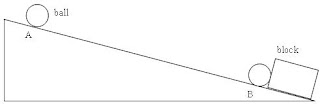
A small ball rolls down a slope AB which is 15 m long. It starts from rest at point A, accelerates uniformly, and takes 5.0 s to reach the bottom at point B. A block is fixed rigidly near point B as shown.
(i) Calculate the average velocity of the ball as it moves down the slope.
(ii) What is its velocity at point B?
(iii) What is its acceleration down the slope?
(iv) At the bottom of the slope, the ball collides with the block and rolls up to a point C before rolling down again. If the speed of the ball just after impact is half of its speed just before the impact, calculate the distance of the point C from A. (Assume that air resistance is negligible.)
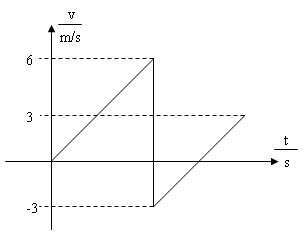
(v) Sketch a graph of velocity against time for the ball showing its velocity from point A to B to C and back to B again.
Answer:
(i) Average velocity = 15 m / 5.0 s = 3 m/s
(ii) For a constant acceleration, s = (v-u)/2 * t => This comes from area under a trapezium in a v-t graph
where
s = 15
t = 5
u = 0
Sub in values, 15 = v/2 * 5
v = 6 m/s
(iii) a = (v-u)/t = 6 / 5 = 1.2 m/s²
(iv) The speed of the ball right after impact is 0.5 * 6 = 3 m/s
Here, we use v² = u² + 2as, where v = 0 (at point C) and a = -1.2 upwards (which is 1.2 downwards from (iii) )
Taking upwards along the slope as positive direction,
and using v² = u² + 2as:
0² = 3² + 2 * (-1.2) * s
s = 3.75 m
Distance of Point C from A = 3.75 m
(v)