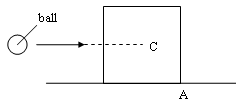
In a children's game, small balls are thrown at wood blocks in order to turn them over. One such block, of mass 150g with each side of length 10cm, is shown in the figure below.
In order to turn the block over, the centre of gravity C of the block must raised so that C is vertically above the corner A as shown below.
(i) For the block as shown in the above figure
(1) Calculate the vertical heigh through which the centre of gravity has been raised.
(2) show that the gain in potential energy of the block is approximately 0.031 J
(ii) The block is struck by a ball of mass 11 g travelling horizontally towards C, as shown below.
The collision is perfectly elastic and, without sliding, the block turns about the corner A. The block is just able to reach the position in the 2nd figure (with C directly above A). 25% of the kinetic energy of the ball is transferred to the block. Calculate
(1) the kinetic energy of the ball just before it strikes the block,
(2) the speed with which the ball strikes the block,
(3) the speed with which the ball rebounds from the block.
(iii) For the collision in (ii) of the ball with the block, calculate
(1) the change in momentum of the ball,
(2) the average force on the block, assuming the ball and the block are in contact for 0.15 s.
*************************
Answer:
(i)
(1) Distance between C and A = ½ √(10² + 10²) = 7.07 cm
=> vertical height in first diagram is 5 cm
=> vertical height in 2nd diagram is 7.07 cm
the centre of gravity has been raised by 7.07 cm -5 cm = 2.07 cm
(2) Gain in G.P.E. = mgh
= (150 * 10-3) (9.81) (2.07 / 100)
= 0.031 J (2 s.f.)
(ii)
(1) Let K = the kinetic energy of the ball just before it strikes the block. Since 25% of K is transferred to the block
=> 0.25 K = Gain in potential energy of the block
=> 0.25K = 0.031 => K = 0.124 J
(2) Let u = speed with which ball strikes the block.
K = ½ mu² => u = √(2K/m) = √(2 * 0.124 / (11 * 10-3))
u = 4.75 ms-1
(3) After the collision, kinetic energy of ball = 0.75K
Let v = speed with which ball rebounds from block
0.75K = ½ mv² => v = √(2*0.75K/m)
v = = √(2 * 0.75 * 0.124 / (11 * 10-3))
v = 4.11 ms-1
(iii)
(1) change in momentum of ball = mv - mu
= m (v - u)
= (11 * 10-3) (4.11 - 4.75)
= -7.04 * 10-3 kg ms-1
(2) By Newton's 2nd Law,
Force on the ball = Rate of change of momentum of ball
By Netwon's 3rd law,
Force on the block = force on the ball (numerically)
= rate of change of momentum of ball
= -7.04 * 10-3 / 0.15
= 0.047 N